Video
- Concept of the week: Hive Partitioning (1152s)
- PR of the week: PR 223 Add system.sync_partition_metadata procedure to sync Hive table partitions (1760s)
- PR Demo: system.sync_partition_metadata procedure demo (2097s)
- Question of the week: Why am I getting, 'Query exceeded maximum columns.' error? (3656s)
Audio
In this week’s concept, Manfred discusses Hive Partitioning.
- Concept from RDBMS systems implemented in HDFS
- Normally just multiple files in a directory per table
- Lots of different file formats, but always one directory
- Partitioning creates nested directories
- Needs to be set up at start of table creation
- CTAS query
- Uses WITH ( partitioned_by = ARRAY[‘date’])
- Results in tablename/date=2020-11-19
- Can also nest deeper WITH ( partitioned_by = ARRAY[‘date’, ‘countrycode’])
- Can greatly enhance performance
- Optimizer can determine what directories to read based on field
- Especially useful when fields are used in WHERE clauses
- Also useful for historic data management over time such as moving data out to archive, deleting data, or replacing data with aggregates, or even just running compaction on subsets
- Presto can use DELETE on partitions using DELTE FROM table WHERE date=value
- Also possible to create empty partitions upfront CALL system.create_empty_partition
See here for more details: https://www.educba.com/partitioning-in-hive/
In this week’s pull request https://github.com/trinodb/trino/pull/223, came from contributor Hao Luo. What this function does is similar to Hive’s MSCK REPAIR TABLE where if it finds a hive partition directory in the filesystem that exist but no partition entry in the metastore, then it will add the entry to the metastore. If there is an entry in the metastore but the partition was deleted from the filesystem, then it will remove the metastore entry. You can find more information about this procedure in the documentation.
Here are the commands and SQL I ran during the show on Presto
SHOW CATALOGS;
SHOW SCHEMAS in minio;
SHOW TABLES IN minio.part;
CREATE SCHEMA minio.part
WITH (location = 's3a://part/');
-- Create a table with no partitions
CREATE TABLE minio.part.no_part (id int, name varchar, dt varchar)
WITH (
format = 'ORC'
);
INSERT INTO minio.part.no_part
VALUES
(1, 'part-1', '2020-11-18'),
(2, 'part-2', '2020-11-18'),
(3, 'part-3', '2020-11-19'),
(4, 'part-4', '2020-11-19'),
(5, 'part-5', '2020-11-20'),
(6, 'part-6', '2020-11-20');
CREATE TABLE minio.part.orders (id int, name varchar, dt varchar)
WITH (
format = 'ORC',
partitioned_by = ARRAY['dt']
);
INSERT INTO minio.part.orders
VALUES
(1, 'part-1', '2020-11-18'),
(2, 'part-2', '2020-11-18'),
(3, 'part-3', '2020-11-19'),
(4, 'part-4', '2020-11-19'),
(5, 'part-5', '2020-11-20'),
(6, 'part-6', '2020-11-20');
SELECT *
FROM minio.part.no_part
WHERE dt = '2020-11-20';
SELECT *
FROM minio.part.orders
WHERE dt = '2020-11-20';
DELETE FROM minio.part.orders
WHERE dt = '2020-11-18';
SELECT *
FROM minio.part.orders;
-- Make sure you are using minio (which is a rename of hive) catalog
CALL system.sync_partition_metadata('part', 'orders', 'ADD');
CALL system.sync_partition_metadata('part', 'orders', 'DROP');
CALL system.sync_partition_metadata('part', 'orders', 'FULL');
-- Create a table with multi partitions
CREATE TABLE minio.part.multi_part (id int, name varchar, year varchar, month varchar, day varchar)
WITH (
format = 'ORC',
partitioned_by = ARRAY['year', 'month', 'day']
);
INSERT INTO minio.part.multi_part
VALUES
(1, 'part-1', '2020', '11', '18'),
(2, 'part-2', '2020', '11', '18'),
(3, 'part-3', '2020', '11', '19'),
(4, 'part-4', '2020', '11', '19'),
(5, 'part-5', '2020', '11', '20'),
(6, 'part-6', '2020', '11', '20'),
(7, 'part-7', '2019', '11', '18'),
(8, 'part-8', '2019', '01', '18'),
(9, 'part-9', '2019', '11', '19'),
(10, 'part-10', '2019', '01', '19'),
(11, 'part-11', '2019', '11', '20'),
(12, 'part-12', '2019', '01', '20');We ran some queries against the metastore database. It’s a complicated model so here is a database diagram to show the different tables and their relations in the metastore.
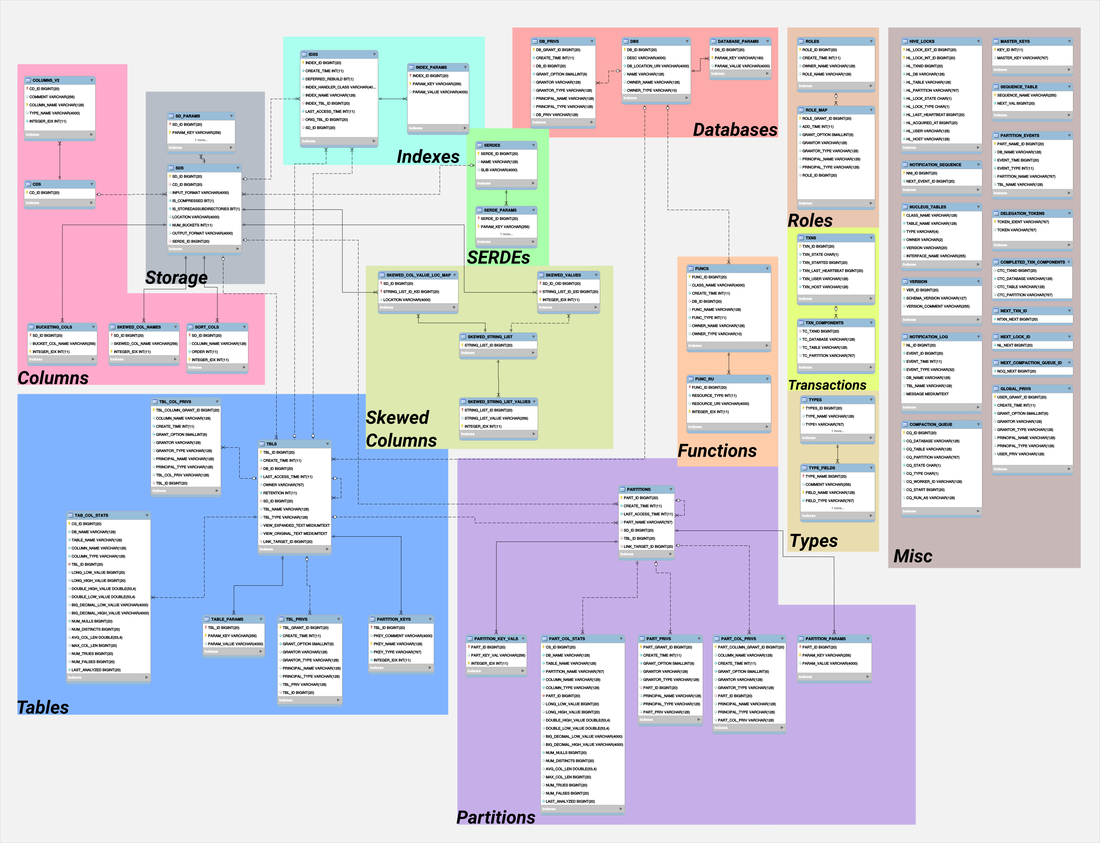 This diagram was generated by niftimusmaximus on
The Analytics Anvil.
This diagram was generated by niftimusmaximus on
The Analytics Anvil.
MariaDB (metastore database)
USE metastore_db;
-- show database
SELECT * FROM DBS;
-- show tables given a database
SELECT t.*
FROM DBS d
JOIN TBLS t ON d.DB_ID = t.DB_ID
WHERE d.NAME = 'part';
-- show location and input format of the table given database/table names
SELECT s.SD_ID, s.INPUT_FORMAT, s.LOCATION, s.SERDE_ID
FROM DBS d
JOIN TBLS t ON d.DB_ID = t.DB_ID
JOIN SDS s ON t.SD_ID = s.SD_ID
WHERE t.TBL_NAME = 'orders' AND d.NAME='part';
-- show (de)serializer format of the table given database/table names
SELECT sd.SERDE_ID, sd.NAME, sd.SLIB
FROM DBS d
JOIN TBLS t ON d.DB_ID = t.DB_ID
JOIN SDS s ON t.SD_ID = s.SD_ID
JOIN SERDES sd ON s.SERDE_ID = sd.SERDE_ID
WHERE t.TBL_NAME = 'orders' AND d.NAME='part';
-- show columns of the table given database/table names
SELECT c.*
FROM DBS d
JOIN TBLS t ON d.DB_ID = t.DB_ID
JOIN SDS s ON t.SD_ID = s.SD_ID
JOIN COLUMNS_V2 c ON s.CD_ID = c.CD_ID
WHERE t.TBL_NAME = 'orders' AND d.NAME='part'
ORDER by CD_ID, INTEGER_IDX;
-- show partitions of the table given database/table names
SELECT p.*, s.LOCATION
FROM DBS d
JOIN TBLS t ON d.DB_ID = t.DB_ID
JOIN PARTITIONS p ON t.TBL_ID = p.TBL_ID
JOIN SDS s ON p.SD_ID = s.SD_ID
WHERE t.TBL_NAME = 'orders' AND d.NAME='part';In this week’s question, we answer:
Why am I getting, “Query exceeded maximum columns. Please reduce the number of columns referenced and re-run the query.”?
Example:
I’m running this query to check for duplicates. My table has approx. 650 columns and I get this error.
SELECT *, COUNT(1)
FROM tbl
GROUP BY *
HAVING COUNT(1) > 1
getting a stacktrace like this
io.prestosql.spi.PrestoException: Compiler failed
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.LocalExecutionPlanner$Visitor.visitScanFilterAndProject(LocalExecutionPlanner.java:1306)
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.LocalExecutionPlanner$Visitor.visitProject(LocalExecutionPlanner.java:1185)
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.LocalExecutionPlanner$Visitor.visitProject(LocalExecutionPlanner.java:705)
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.plan.ProjectNode.accept(ProjectNode.java:82)
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.LocalExecutionPlanner$Visitor.visitAggregation(LocalExecutionPlanner.java:1119)
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.LocalExecutionPlanner$Visitor.visitAggregation(LocalExecutionPlanner.java:705)
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.plan.AggregationNode.accept(AggregationNode.java:204)
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.LocalExecutionPlanner.plan(LocalExecutionPlanner.java:461)
at io.prestosql.sql.planner.LocalExecutionPlanner.plan(LocalExecutionPlanner.java:432)
at io.prestosql.execution.SqlTaskExecutionFactory.create(SqlTaskExecutionFactory.java:75)
at io.prestosql.execution.SqlTask.updateTask(SqlTask.java:382)
at io.prestosql.execution.SqlTaskManager.updateTask(SqlTaskManager.java:383)
at io.prestosql.server.TaskResource.createOrUpdateTask(TaskResource.java:128)
at jdk.internal.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor480.invoke(Unknown Source)
The throwable that causes this error MethodTooLargeException comes from the ASM
library https://asm.ow2.io/ when you ask it to create a method with more
bytecode than is allowed by the JVM specification.
We try to generate code for handling given query and the code generated is too large. Since the code is proportional to number of columns referenced, we rewrap the exception in something more meaningful to the user.
The general strategy would be to lower the number of columns that you reference.
The problem is that in removing columns you will remove important information to the query. For example, in the example looking for duplicates above, you won’t be able to discard false positive duplicate matches, but this may be good enough to help narrow the search space. As always, it depends…
To learn more about the JVM limit and search for code_length in the Java SE specification.
Special thanks to Ashhar Hasan for asking this question and providing some useful context!
Release Notes discussed: https://trino.io/docs/current/release/release-346.html
Manfred’s Training - SQL at any scale https://www.simpligility.com/2020/10/join-me-for-presto-first-steps/ https://learning.oreilly.com/live-training/courses/presto-first-steps/0636920462859/
Blogs
- https://www.javahelps.com/2020/05/presto-sql-for-newbies.html
- https://www.javahelps.com/2020/04/setup-presto-sql-development-environment.html
- https://www.javahelps.com/2019/11/presto-sql-types-of-joins.html
- https://www.javahelps.com/2019/11/presto-sql-join-algorithms.html
- https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/deploying-starburst-enterprise-presto-on-googles-kubernetes-engine-with-storage-and-postgres-72483b10ab62
Upcoming events
- Nov 19 Presto Tokyo Conference - Japanese https://techplay.jp/event/795265
- Nov 24 EMEA - Polish https://www.meetup.com/Warsaw-Data-Engineering/events/274666392/
- Dec 2 https://www.evanta.com/cdo/atlanta/2020-atlanta-cdo-virtual-executive-summit
- Dec 3 EMEA https://www.starburstdata.com/introduction-to-presto/
- Dec 9 https://techtalksummits.com/event/virtual-commercial-it-providence-ri/
- Dec 10 https://techtalksummits.com/event/virtual-commercial-it-denver-co/
- Dec 10 https://www.evanta.com/cdo/san-francisco/2020-san-francisco-cdo-virtual-executive-summit
- Dec 16 https://www.evanta.com/cdo/boston/2020-boston-cdo-virtual-executive-summit
Latest training from David, Dain, and Martin(Now with timestamps!):
- https://trino.io/blog/2020/07/15/training-advanced-sql.html
- https://trino.io/blog/2020/07/30/training-query-tuning.html
- https://trino.io/blog/2020/08/13/training-security.html
- https://trino.io/blog/2020/08/27/training-performance.html
Presto Summit Series - Real world usage
- https://trino.io/blog/2020/05/15/state-of-presto.html
- https://trino.io/blog/2020/06/16/presto-summit-zuora.html
- https://trino.io/blog/2020/07/06/presto-summit-arm-td.html
- https://trino.io/blog/2020/07/22/presto-summit-pinterest.html
Recent Podcasts:
- https://www.contributor.fyi/presto
- https://www.dataengineeringpodcast.com/presto-distributed-sql-episode-149/
If you want to learn more about Presto yourself, you should check out the O’Reilly Trino Definitive guide. You can download the free PDF or buy the book online.
Music for the show is from the Megaman 6 Game Play album by Krzysztof Słowikowski.